Understanding Barrett's Esophagus and Lansoprazole
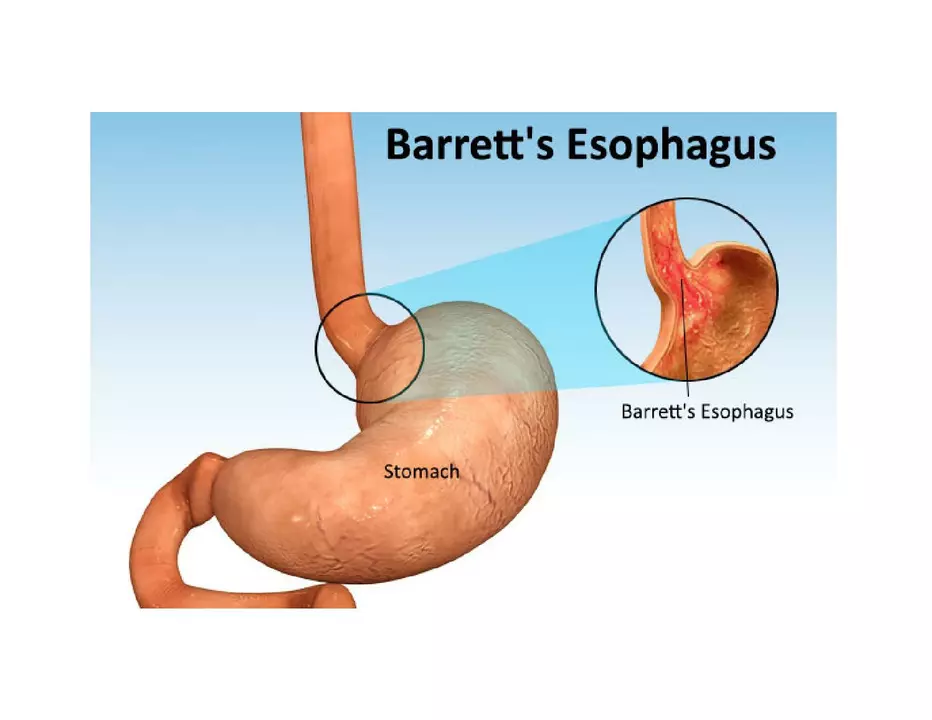
Before diving into the effectiveness of Lansoprazole in treating Barrett's esophagus, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of what Barrett's esophagus is and how it affects the body. Barrett's esophagus is a condition where the normal lining of the esophagus is replaced by tissue similar to the lining of the intestine. This change in the esophageal lining is mainly caused by long-term exposure to stomach acid, often occurring in people with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Lansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that is commonly prescribed to treat GERD, stomach ulcers, and other related conditions. By reducing the production of stomach acid, Lansoprazole helps alleviate symptoms and allows the esophagus to heal. This article will delve into the effectiveness of Lansoprazole for treating Barrett's esophagus and explore the benefits and potential drawbacks of using this medication.
Lansoprazole's Role in Reducing Acid Reflux Symptoms
One of the primary reasons Lansoprazole is prescribed for patients with Barrett's esophagus is its ability to alleviate symptoms of acid reflux. By inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach, Lansoprazole effectively reduces the production of stomach acid. This, in turn, helps prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus, which can cause inflammation and damage to the esophageal lining. In doing so, Lansoprazole can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with Barrett's esophagus by reducing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
Furthermore, by reducing the production of stomach acid, Lansoprazole creates an environment in which the esophagus can heal from previous acid-related damage. This healing process is crucial in preventing further damage and reducing the risk of complications associated with Barrett's esophagus.
Preventing Progression to Esophageal Cancer
One of the most significant concerns for individuals with Barrett's esophagus is the increased risk of developing esophageal cancer. Studies have shown that people with Barrett's esophagus are at a higher risk of developing a type of esophageal cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma. By reducing stomach acid production and promoting the healing of the esophageal lining, Lansoprazole may play a vital role in preventing the progression of Barrett's esophagus to esophageal cancer.
While further research is needed to definitively establish the relationship between PPIs like Lansoprazole and the prevention of esophageal cancer, several studies have shown promising results. These studies suggest that patients with Barrett's esophagus who take PPIs may have a lower risk of developing esophageal cancer compared to those who do not take PPIs.
Reducing the Risk of Esophageal Strictures
Another potential benefit of using Lansoprazole to treat Barrett's esophagus is the reduction of esophageal strictures. Esophageal strictures are a narrowing of the esophagus, which can cause difficulties in swallowing and increase the risk of food becoming lodged in the throat. By reducing acid reflux and promoting the healing of the esophageal lining, Lansoprazole may help prevent the development of esophageal strictures in patients with Barrett's esophagus.
While esophageal strictures can often be treated with dilation procedures, preventing their development in the first place is undoubtedly more desirable. Therefore, the use of Lansoprazole in treating Barrett's esophagus may provide patients with significant long-term benefits by reducing the risk of these complications.
Considering the Side Effects of Lansoprazole
While Lansoprazole has proven to be effective in treating Barrett's esophagus and reducing the associated risks, it is essential to consider the potential side effects of this medication. Some common side effects of Lansoprazole include headache, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Although these side effects are typically mild and resolve on their own, they may be a concern for some individuals.
Additionally, long-term use of PPIs like Lansoprazole has been associated with an increased risk of certain health issues, such as bone fractures, vitamin B12 deficiency, and kidney disease. It is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to weigh the benefits of Lansoprazole against the potential risks and side effects when determining the most appropriate treatment plan for managing Barrett's esophagus.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
As with any medical treatment, it is essential to monitor the progress and effectiveness of Lansoprazole in treating Barrett's esophagus. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are necessary to assess the patient's response to the medication and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. This may include changing the dosage of Lansoprazole, trying alternative medications, or exploring additional treatment options such as endoscopic therapy or surgery.
In conclusion, Lansoprazole is an effective medication for treating Barrett's esophagus and reducing the associated risks and complications. However, it is essential to consider the potential side effects and closely monitor the patient's progress to ensure the most successful treatment outcome. Working closely with a healthcare provider and following a personalized treatment plan is the key to managing Barrett's esophagus and improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.

I've been on lansoprazole for 5 years for my GERD, and yeah, it's kept the heartburn under control. But I swear, my bones feel more brittle lately. Got a DEXA scan last month-T-score was borderline. Wonder if it's the PPI or just aging.