Understanding Parkinson's Disease and Occupational Therapy
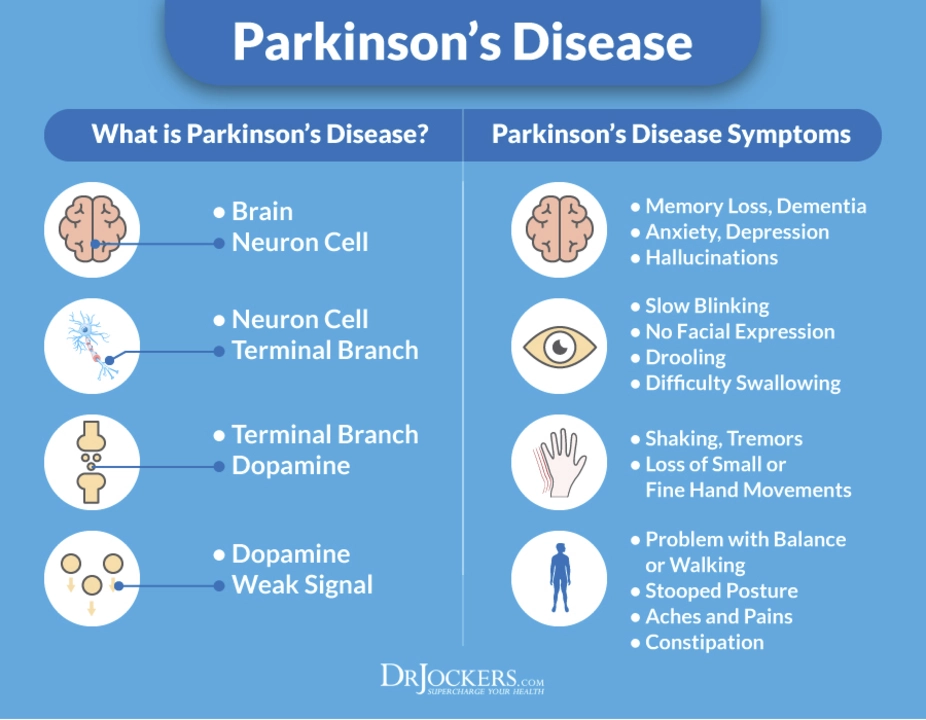
Before diving into the role of Trihexyphenidyl in occupational therapy for Parkinson's Disease, it's important to first understand the basics of this neurological condition and the role of occupational therapy in its management. Parkinson's Disease is a progressive, degenerative disorder that affects the central nervous system, specifically the area of the brain responsible for controlling movement. As a result, individuals with Parkinson's often experience symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, balance problems, and difficulty with everyday tasks.
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals with Parkinson's Disease maintain their independence and improve their quality of life. Occupational therapists work with patients to develop strategies and adapt their environment to compensate for their movement difficulties. This can include recommending assistive devices, teaching new ways to perform daily tasks, and suggesting home modifications to improve safety and accessibility.
Trihexyphenidyl: An Overview and its Use in Parkinson's Disease
Trihexyphenidyl is a medication that has been used for many years in the treatment of Parkinson's Disease. It belongs to a class of drugs called anticholinergics, which work by blocking the action of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In Parkinson's Disease, there is an imbalance between the neurotransmitters dopamine and acetylcholine, leading to the hallmark symptoms of the condition. By blocking the action of acetylcholine, Trihexyphenidyl helps to restore balance in the brain, reducing symptoms such as tremors and muscle stiffness.
While Trihexyphenidyl is not a cure for Parkinson's Disease, it can help to manage and alleviate some of the symptoms, making daily activities easier for those affected. It is often used in conjunction with other medications, such as levodopa, to provide optimal symptom control.
Integrating Trihexyphenidyl into Occupational Therapy Interventions
As an occupational therapist working with individuals with Parkinson's Disease, it's essential to be aware of the medications your clients are taking, including Trihexyphenidyl. Understanding the effects of this medication on their symptoms can help you tailor your interventions to best meet their needs. For example, if you know that a client is taking Trihexyphenidyl and their tremors have been reduced, you might focus more on improving their fine motor skills or addressing balance and mobility issues.
Additionally, knowing that a client is on Trihexyphenidyl can help you anticipate potential side effects, such as drowsiness, dry mouth, or blurred vision. By being aware of these potential issues, you can adjust your therapy sessions accordingly and provide appropriate recommendations for managing these side effects.
Addressing Potential Side Effects of Trihexyphenidyl in Therapy
As with any medication, Trihexyphenidyl can cause side effects that may impact an individual's ability to participate in occupational therapy sessions. Some common side effects of Trihexyphenidyl include dry mouth, blurred vision, drowsiness, dizziness, and constipation. As an occupational therapist, it's important to be aware of these potential side effects and to provide appropriate support and recommendations to help your clients manage them.
For example, if a client is experiencing dry mouth due to Trihexyphenidyl, you might suggest they keep a water bottle nearby during therapy sessions and take frequent sips to stay hydrated. If blurred vision is an issue, you could recommend strategies such as using a magnifying glass, increasing lighting, or using high-contrast materials during activities.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Trihexyphenidyl in Therapy
As an occupational therapist, it's important to continually evaluate the effectiveness of your clients' medications, including Trihexyphenidyl, to ensure they are receiving optimal symptom management. This can involve monitoring changes in their symptoms, such as reductions in tremors or improvements in mobility, and adjusting therapy interventions accordingly. Additionally, it's important to discuss any observed changes or concerns with your client's healthcare team, as they may need to adjust the medication dosage or consider alternative treatments.
By closely monitoring the effects of Trihexyphenidyl on your clients, you can help ensure they are receiving the best possible care and support in managing their Parkinson's Disease symptoms.
Collaborating with the Healthcare Team
Managing Parkinson's Disease is a team effort, and as an occupational therapist, you play a vital role in that team. Collaborating with your clients' healthcare team, including their neurologist, primary care physician, and other therapists, can help ensure a comprehensive and coordinated approach to their care. This includes sharing information about the effects of Trihexyphenidyl on their symptoms, discussing any observed side effects, and adjusting therapy interventions based on changes in their medication regimen.
By working closely with the healthcare team and staying informed about your clients' medications, including Trihexyphenidyl, you can help provide the best possible support and care for individuals with Parkinson's Disease.

Trihexyphenidyl’s like that one weird uncle who shows up to family dinners and somehow makes everything less shaky. Not the life of the party, but you’re glad he’s there when your hands start doing the cha-cha. Occupational therapists? They’re the ones who figure out how to make your uncle useful without letting him spill gravy on the rug.