Effectiveness: How Well Treatments and Meds Work
Some treatments look great on paper but don’t help you in real life. This tag gathers articles that test whether drugs and therapies actually do what they promise — from antivirals for chickenpox to blood thinners and inhaler swaps. If you want straight answers about whether a medicine works, how much it helps, and who benefits most, you’re in the right place.
How we judge effectiveness
Start by asking one simple question: did the study measure something that matters to you? A change in lab numbers isn’t the same as feeling better, avoiding hospital visits, or living longer. We look for randomized controlled trials (the gold standard), systematic reviews, or large observational studies when RCTs aren’t available. Bigger sample sizes and longer follow-up time usually give more reliable results.
Also check what outcome they measured. For example, a diabetes drug that cuts A1c by 0.3% might be statistically significant but not noticeable in daily life. Contrast that with a medication that reduces hospitalizations or prevents strokes — those are meaningful wins. Side effects matter too: a medicine can be effective but unsafe or poorly tolerated for some people.
Finally, watch for bias. Who funded the study? Did researchers report all outcomes? We call out conflicts and point readers to independent evidence when possible.
Use these articles to answer your questions
Want practical help reading research? Look for sections in our articles that summarize the evidence, list real numbers (like % benefit or risk), and explain who was studied. If a piece compares alternatives, pay attention to cost, availability, and typical side effects — not just which drug wins on paper.
Here are quick examples you can find under this tag: famciclovir for chickenpox (how strong is the evidence?), Plavix basics (who benefits and who doesn’t?), inhaler alternatives to Symbicort (practical cost and insurance tips), and safety notes like albendazole in pregnancy. Each write-up points out the study type, main results, and what a typical patient might expect.
If you’re trying to decide about a specific medicine: bring the facts to your prescriber. Share the outcome that matters to you (pain relief, fewer attacks, fewer hospital visits), ask how the study population compares to you, and discuss side effect trade-offs. If cost or access is an issue, our articles often list lower-cost alternatives or tips to save on common meds.
Questions or want a topic covered? Use our contact page and tell us what you need. We aim to make evidence useful — not confusing — so you can make safer, smarter choices about treatments that affect your life.
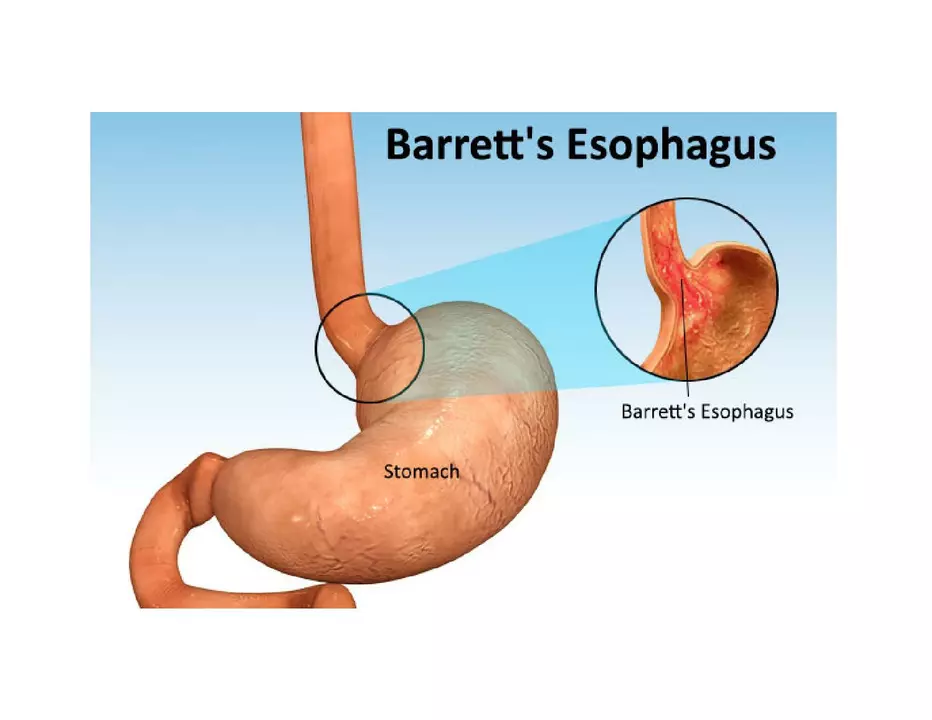
The effectiveness of Lansoprazole for treating Barrett's esophagus
I recently came across some interesting information about the effectiveness of Lansoprazole in treating Barrett's esophagus. It appears that this medication, which belongs to the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) family, can significantly reduce the production of stomach acid and alleviate symptoms associated with Barrett's esophagus. Moreover, Lansoprazole has shown promising results in preventing the progression of this condition to esophageal cancer. However, it is important to remember that while Lansoprazole can be an effective treatment option, it may not work for everyone and should be taken under the guidance of a medical professional. Overall, it's fascinating to learn about the potential benefits of this medication in managing Barrett's esophagus and improving the quality of life for those affected.
More Detail